
The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is the primary agency to oversee all things chemical management in the European Union. They deal with hazardous chemicals and mixtures sold on the EU market, regulate substances of very high concern to human health and environmental safety, as well as receive poisons centre notifications.
ECHA is also the overseeing body of the Classification, Labelling, and Packaging (CLP) Regulation in the EU, providing policy updates and guidance to chemical manufacturers and distributors. ECHA ensures that every manufacturer, supplier, seller, and consumer is on the same page as far as chemical hazards are concerned. This is where Harmonised Classification and Labelling becomes essential.

The Classification, Labelling and Packaging (CLP) Regulation ((EC) No 1272/2008) is based on the United Nations’ Globally Harmonised System (GHS). Its purpose is to ensure a high level of protection to health and the environment, as well as the free movement of substances, mixtures, and articles within the EU. CLP dictates the classification and labelling of hazardous goods based on the table of harmonised entries in Annex VI to CLP.
In general, a CLP-abiding label must display certain label elements from the UN GHS system, including hazard pictogram(s), signal word, hazard, and precautionary statements, along with any supplemental information reflecting the assigned classification of the substance or mixture.
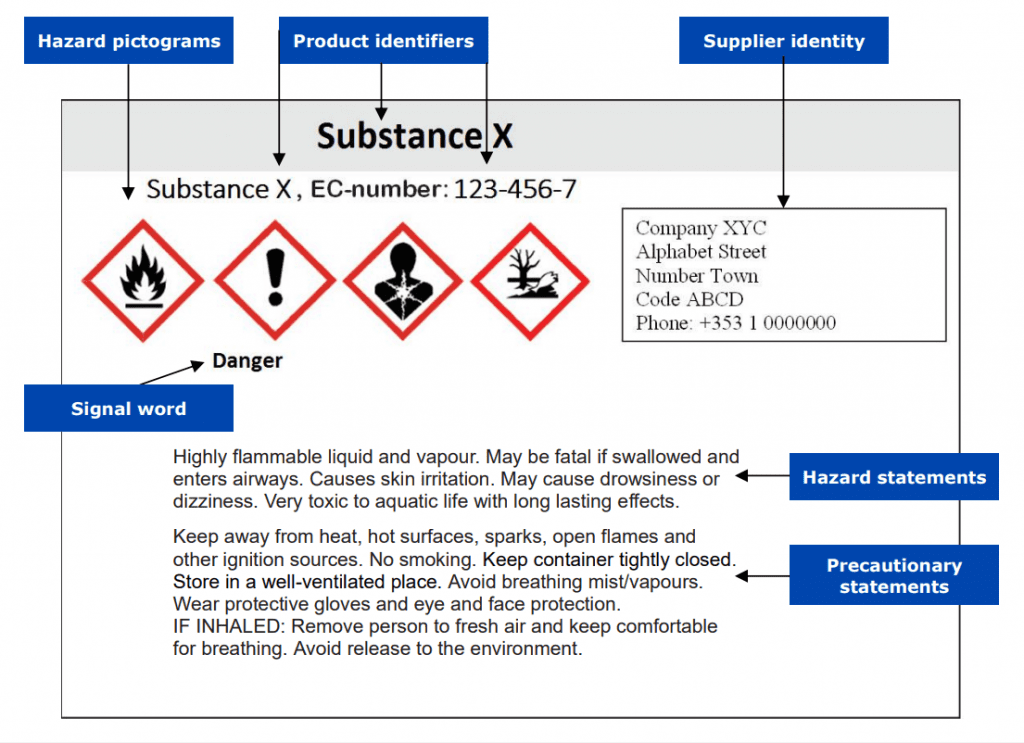
Harmonised Classification and Labelling (CLH) is a regulatory framework created by ECHA in order to coordinate the classification and labelling of all hazardous substances on the market in the EU, and to ensure adequate risk management for these substances.
Annex VI to the CLP Regulation provides a comprehensive list of all harmonised substance entries, listing over 4000 substances. A complete (unofficial) list is available on the ECHA website in an Excel spreadsheet for suppliers and distributors to easily access, however the formalised version of the harmonised entries can be found in the Official Journal of the European Union.
For each entry in the list, Annex VI provides the following information (where applicable):
Notes are indicated by letters and/or numbers, which are further specified in the official Annex VI Journal document.
Notes A through to U can specify different properties or preparations applicable to different substance classes which may change the CLP requirements. For example, Note F specifies that “This substance may contain a stabiliser. If the stabiliser changes the hazardous properties of the substance, as indicated by the classification in Part 3, classification and labelling should be provided in accordance with the rules for classification and labelling of hazardous mixtures.”
Notes 1 through 7 list specifications related to labelling conventions, most often in relation to substance concentration. For example, Note 5 specifies that “the concentration limits for gaseous mixtures are expressed as volume per volume percentage.”
The harmonised classification and labelling system has been put in place to ensure that the risk presented by any and all hazardous substances distributed in the EU are consistent and accounted for.
Labelling in accordance with CLP is required when:
Each year ECHA adopts the Adaptation to Technical Progress, which includes updates and amendments to CLP Regulation. Often, but not always, this includes updates to Annex VI and the harmonised classifications table. This ensures that CLP is evolving alongside the industry and that, with harmonised classification, concern for human health and environmental safety is paramount.
At Chemwatch, we manage our own comprehensive regulatory and chemical database, informed by over 30 years of chemical expertise—and we are well equipped to help you with all of your chemical regulation needs. Contact us today for help regarding your chemical labelling, Risk Assessment, SDS management, and more! You can also email us directly at sa***@*******ch.net.
Sources: